Peptide Bond Is Found in Which Type of Biological Molecule
As we noted for nucleic acids a polymer is a chain of subunits monomers linked together by chemical bonds. An amino acid polymer is known as a polypeptide.
Peptide Types And Functions Online Biology Notes
To generate a polypeptide new amino acids are added exclusively to the C-terminal end of the polymer.

. Nucleic acids possess phosphodiester bonds that is present between carbon atoms of adjacent sugar molecules in. The peptide bond is planar and has two states. Peptide bonds are broken down during the process of protein degradation.
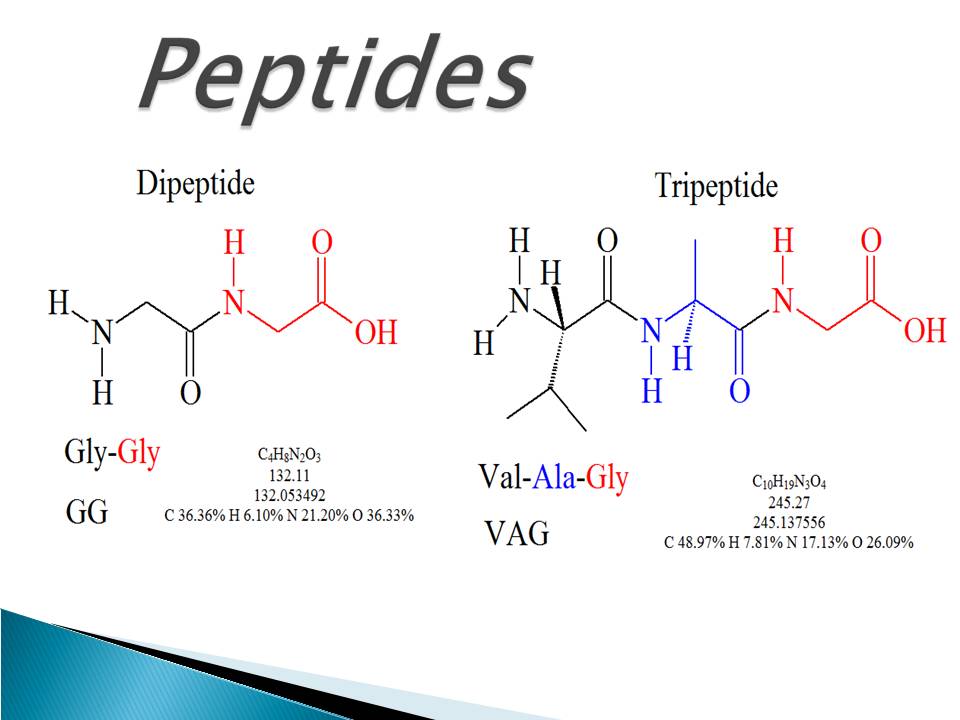
A peptide bond is the kind of bond formed between amino acids. As in the case of each amino acid the dipeptide has an N-terminal amino end and a C-terminal carboxylic acid end. The bond between two amino acids is known as a peptide bond.
Carbohydrates possess glycosidic linkages between two monosaccharides. A peptide bond is found in proteins between two amino acids. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed between the carboxyl group of amino acid 1 and the amino group of amino acid 2.
The structure of a peptide can be written fairly easily without showing the complete amide synthesis reaction by learning the structure of the backbone for peptides and proteins. N-H 2 CH C double bond O. Carbohydrates possess glycosidic linkages between two monosaccharides.
These occur in polypeptides. Protein is very important for our body as it forms the structural components of our cells. The peptide bond is also referred to as the isopeptide bond where the amide bond forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of.
This linkage is found along a peptide or protein chain. Backbone Peptide or Protein Structure. A peptide bond sometimes mistakenly called amino bond is a covalent bond that is formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the another molecule releasing a molecule of water.
A water molecule is eliminated when a peptide bond is formed. A peptide bond is found in which type of biological molecule. The peptide backbone consists of repeating units of N-H 2 CH C double bond O.
A peptide bond is found in proteins between two amino acids. Molecule formed from two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond is known as a dipeptide. Two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond is known as a dipeptide.
Proteins are used in many roles including structural support catalyzing important reactions and recognizing molecules in the environment. Peptide Bond Definition Biology. Lipids possess ester bonds which are covalent in nature formed during condensation reactions.
During the formation of this bond there is a release of water H 2 O molecules. What type of bonds link individual amino acids together. A peptide bond is the kind of bond formed between amino acids.
Trans ω 180 and cis ω 0. A glycosidic bond is a bond present in disaccharides and polysaccharides. A peptide bond is a covalent bond and can be broken by hydrolyzing it.
The result is C-N bond to link the two amino acids together to form a. A peptide bond is basically an amide-type of covalent chemical bond. This is a a condensation reaction and usually occurs between amino acids.
In most cases the peptide bonds in proteins are trans. Peptide bond is found in proteins peptones polypeptides and dipeptides etc. Peptide bonds are usually amide bonds -CONH between the -COOH group and the NH 2 group of the contiguous amino acids.
This is a bond formed between two adjacent monosaccharides. A peptide bond is an amide bond -CONH between the NH 2 group and the COOH group of adjacent amino acids. With the formation of a peptide bond there is the elimination of a water molecule.
Long polypeptides containing more than 20 amino acids are called proteins. Long polypeptides containing more than 20 amino acids are called proteins. Whenever the two amino acids are joined the bond between them is called a polypeptide.
Lipids possess ester bonds which are covalent in nature formed during condensation reactions. A couple of amino acids formed a covalent bond between them which is called a peptide bond. A polypeptide can be composed of 20 different possible monomers.
In the trans configuration the two alpha carbon atoms of the connected amino acids are on the opposite sides of the peptide bond whereas in cis configuration they are on the same side of the peptide bond. Amino acids join together by peptide bonds to form a polymer known as protein. A peptide bond is a special type of amide bond formed between two molecules where an α-carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the α-amino group of another molecule releasing a water molecule.
Nucleic acids possess phosphodiester bonds that is present between carbon atoms of adjacent sugar molecules in. In the learn based tool prompt with term and copy the whole answer and paste it into the answer box. The chapter is number 3 titled The Chemistry of Organic Molecules.
This bond links two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 carbon number one of one alpha-amino acid and N2 nitrogen number two of another. A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule releasing a molecule of water H2O. The alpha helix and beta sheet are found at which level of protein organization.
Living organisms use peptide bonds to form long chains of amino acids known as proteins. These occur in polypeptides. A peptide bond is therefore the basis of most biological reactions.
This study guide is based off of Biology by Sylvia Mader 10th edition. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed between two amino acids.

Peptide Bond The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Peptide Bond Definition Structure Mechanism And Examples

Peptide Bond And Other Types Bonds In Biomolecules An Overview
No comments for "Peptide Bond Is Found in Which Type of Biological Molecule"
Post a Comment